Today is Vitamin C Day.
In 2019, a skincare line, SkinCeuticals, created National Vitamin C Day. The aim was to generate awareness around vitamin C. The day also celebrated a research breakthrough. SkinCeuticals established parameters to allow the effective delivery of antioxidants in vitamin C to the skin. The findings proved beyond a doubt the benefits of topical application of vitamin C to the skin.
Much before its official discovery in 1932, health experts determined that citrus fruits could effectively prevent scurvy — a debilitating disease that claimed the lives of millions of sailors from 1500 to 1800. Loading up on vitamin C isn’t a new concept. In the 1970s, double Nobel Laureate Linus Pauling championed daily super doses of oranges to prevent the common cold. He wasn’t wrong about its efficacy but was off the mark in his daily recommended dosage — 12 to 24 oranges a day!
Vitamin C, also called ‘ascorbic acid’, dissolves in water. It remains in our tissues but doesn’t store well in the body. To avoid overdosing on vitamin C, scientists recommend a daily intake of 90 mg for men above 19 years and 75 mg for women. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant. It can heal wounds and control infection. Among others, it’s also responsible for the production of collagen — a crucial structural protein found throughout the connective tissues in our body.
Collagen is a protein that holds our body together, giving it structure and added strength. Our pantries and kitchen shelves already contain some of the best natural sources of vitamin C. Make sure to stock up on citrus fruits like lemon, oranges, and grapefruit that have a ton of vitamin C. Other excellent sources are tomatoes, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, white potatoes, and bell peppers.
The role of Vitamin C in skin.
Normal skin contains high concentrations of vitamin C, with levels comparable to other body tissues and well above plasma concentrations, suggesting active accumulation from the circulation. Several reports have indicated that vitamin C levels are lower in aged or photodamaged skin. Whether this association reflects cause or effect is unknown, but it has also been reported that excessive exposure to oxidant stress via pollutants or UV irradiation is associated with depleted vitamin C levels in the epidermal layer .Indeed, more vitamin C is found in the epidermal layer than in the dermis, with differences of 2–5-fold between the two layers being consistently reported . Levels of vitamin C in skin are similar to the levels of other water soluble antioxidants such as glutathione .There is a suggestion that vitamin C in the stratum corneum layer of the epidermis exists in a concentration gradient. The lowest vitamin C concentration was present at the outer surface of the epidermis, with a sharp increase in concentration in the deeper layers of the stratum corneum, possibly reflecting depletion in the outer cells due to chronic exposure to the environment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5579659/
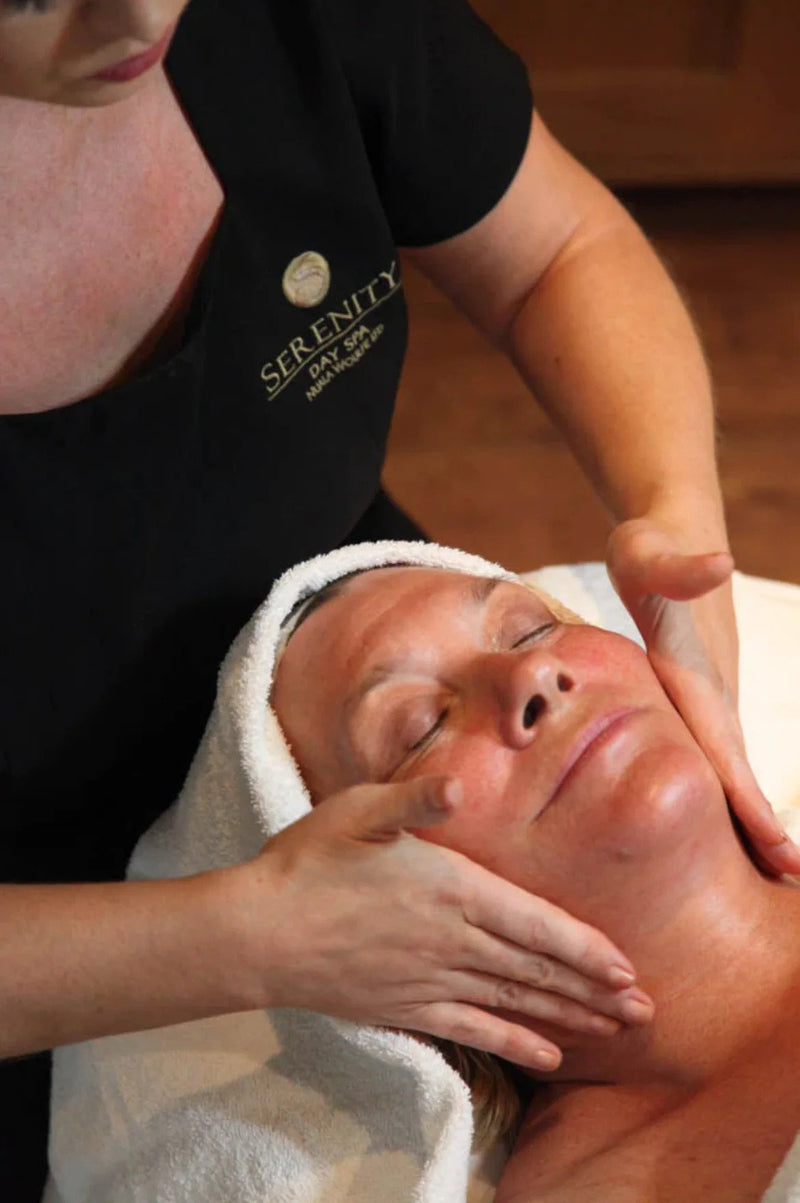
A topical vitamin C used every morning used under a good quality SPF will help to protect the skin against environmental and UV damage.
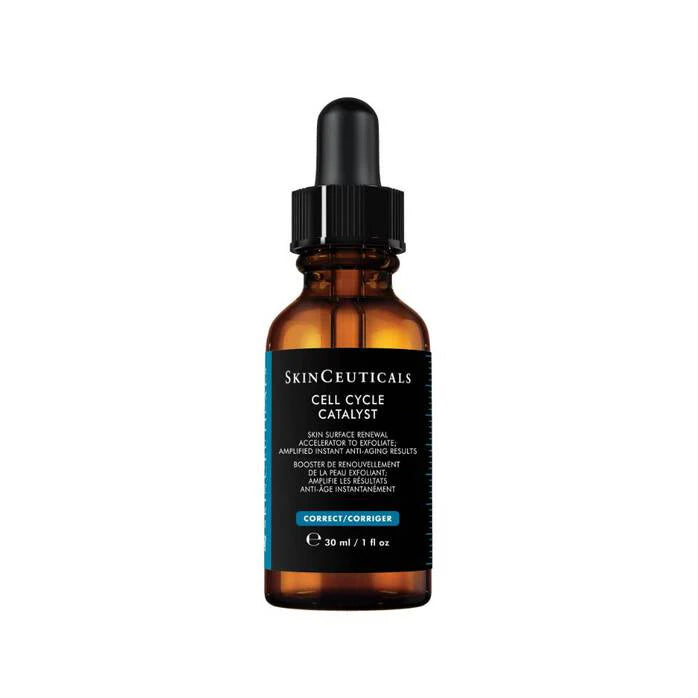
We have kits in stock that combine the highest quality vitamin C with an appropriate SPF to suit the specific skin type, receive a full sized SPF for free in these kits while stocks last.