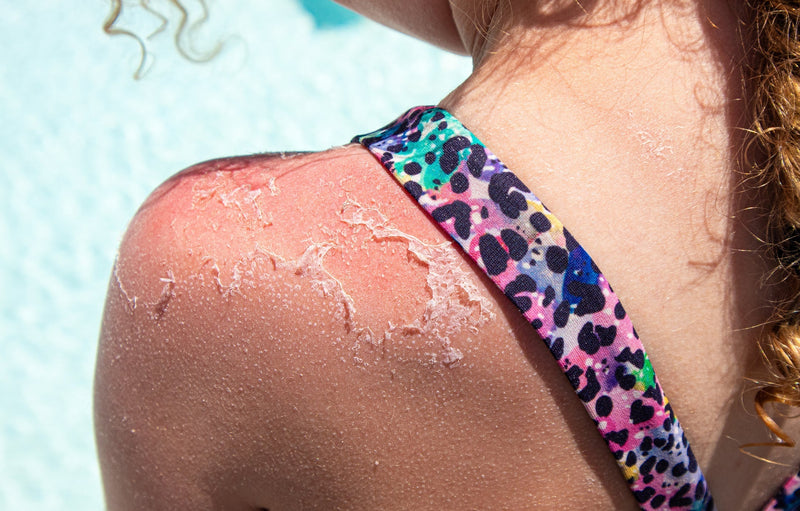
Skin cancer is most diagnosed cancer in Ireland with over 13,000 new cases diagnosed every year. The National Cancer Registry of Ireland expects this number to double by 2040. Skin cancer is a disease of skin cells. Nine out of every 10 cases are caused by UV rays from the sun or sunbed. Why you should apply a stand-alone Day light protection every day even in winter. A Makeup with SPF is not sufficient to protect you against the damage associated with day light.
Sunlight in moderation is good for our wellbeing
Sunlight, in moderation, is good for us, but overexposure to the sun can damage skin both on the surface and at a cellular level. This article looks at the different rays that make up sunlight, examines the positive and negative effects those rays have on skin condition and outlines the factors that influence the way your skin reacts to the sun.
Ultraviolet light is invisible to the human eye and comes in three forms: ultraviolet A (UVA), ultraviolet B (UVB) and ultraviolet C (UVC).
UV light has a shorter wavelength than visible light. UVC rays have the shortest wavelength (of between 100 and 290nm). They are blocked by the earth’s atmosphere and so don’t reach the skin. UVA and UVB rays have a wavelength of between 280nm and 400nm, though UVA has a longer wavelength than UVB. Together they make up about 5% of the sun’s rays.
UVA rays are less intense than UVB, but there are 30 to 50 times more of them. They are also present constantly, with relatively equal intensity, during all daylight hours throughout the year. UVB rays, however, fluctuate throughout the day and are at their strongest at noon. Both pass virtually unhindered through cloud and smog.
Infrared light
Infrared A and B rays have a longer wavelength of between 760nm and 1000nm (1mm) and – like UV rays – are not visible to the human eye. They account for the remaining 45% of light.
High-energy visible light – BLUE LIGHT
High Energy Visible Light (HEVIS Light) is all around us. It’s part of the light we can see. It’s been around for as long as UV rays, but while much has been written about their effect on skin, the molecular and visible effect of HEV Light on skin is a more recent discovery. Research proves that HEVIS light influences skin condition and can cause skin to become photoaged (age prematurely because of sun exposure). We examine the effects HEVIS light has on skin, put it into context alongside UVA and UVB rays and consider how best to protect skin from photoaging.
50% of the sun’s rays are visible
The sunlight spectrum consists of UV, visible and infrared light. Visible light accounts for 50% of the sunlight spectrum and, as the name suggests, it’s the only part of light that can be detected by the human eye (UV and Infrared Light are both invisible).
The blue/violet band of this visible spectrum has a particularly high energy level and is known as High Energy Visible Light. This is often abbreviated to HEV Light or HEVL.
How does HEVIS Light compare to UV rays?
Light is measured in wavelengths, the units of which are nanometres (nm) and millimetres (mm). Visible light has a wavelength range in the region of 400 to 760nm, with HEV light falling somewhere between the 400-500nm mark. UV light has a shorter wavelength (of between 290 and 400nm) though UVA has longer wavelengths than UVB.
Most of the skin damage caused by the sun comes from UV rays and protecting skin from UV should remain the priority when caring for skin in the sun.
How does high-energy visible light affect skin?
Note – it is good in moderation.
Sunlight can be good for us – it’s an important source of Vitamin D which is essential for healthy bones, and it boosts our levels of serotonin, lifting our mood. But too much sun can damage skin. So you might take a supplement of Vitamin D3 combined with K2.
HEVIS Light and UV rays affect skin differently
- While UVB rays penetrate the outermost layers of skin (the epidermis), HEV Light, like UVA rays, penetrates the lower layers of skin (the dermis):
- UVB rays are responsible for sunburn. HEVIS Light has not been associated with sunburn.
- UVB rays and, to a lesser extent, UVA rays have been linked to DNA damage which can cause skin cancer.
- Both UVA rays and HEVIS Light can cause skin to age prematurely (photo age).
- UVA rays are the primary cause of sun allergies. UVB rays can also cause sun allergies, but to a lesser extent.
- UVA, UVB and HEVIS Light can induce hyperpigmentation and may contribute to conditions such as sunspots (also known as age spots), melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
How do the sun’s different rays affect skin?
Sunlight can be good for us, but too much sun causes skin damage. Sunburn, photoaging (premature skin aging caused by the sun), hyperpigmentation and sun allergies are examples of visible skin damage, but the effects of sun exposure can go even deeper, causing DNA damage at a cellular level.
UV rays (both UVA and UVB) are the main cause of sun-induced skin damage but high-energy visible (HEVIS) light can cause further stress to skin.
The rays affect skin in different ways:
UVB rays provide the energy your skin needs to make Vitamin D; they stimulate the production of melanin which is responsible for tanning. They don’t travel as deeply as UVA rays, penetrating only the outermost layers of skin (the epidermis), but they cause more immediate damage such as sunburn and can cause skin to thicken temporarily. UVB rays are directly absorbed by cellular DNA and can lead to skin diseases such as actinic keratosis and skin cancer.
UVB rays (as well as UVA and HEVIS) can induce hyperpigmentation.
How do UVA rays affect skin?
The effects of sunlight exposure on a cellular level
UVA rays penetrate the deeper layers of skin (the dermis). They stimulate the production of free radicals in the skin which cause oxidative stress and can lead to indirect DNA damage: (where the free radicals modify cellular DNA over time). UVA rays are most associated with:
- Photo ageing (premature skin ageing caused by the sun):
- Sun allergies such as PLE (UVB rays can also provoke allergies, but to a lesser degree)
- Hyperpigmentation such as sunspots (also known as age spots)
How does HEVIS light affect skin?
Like UVA, HEVIS light penetrates the deeper layers of skin and generates free radicals that cause oxidative stress. These free radicals are one of the main causes of photoaging. They interfere with skin cells and break down the collagen and elastin that gives skin its plump and youthful appearance. HEVIS light is also linked to hyperpigmentation.
How does the sun cause oxidative stress?
UVA and HEVIS light rays interact with skin cells and generate free radicals. These free radicals are highly reactive oxygen molecules and are also known as ROS – Reactive Oxygen Species. The body uses antioxidants to neutralise these potentially harmful free radicals. When there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralise them, the free radicals start to damage cells in a process known as oxidative stress.
What are the negative effects of sunlight on skin?
Over exposure to the sun is bad for skin and for our health in general. Here are some of the problems it can cause:
The negative effects of sunlight on skin: sunburn
Sunburn is the most common form of sun damage and is caused by UVB rays. It is characterized by red, sore and blistering skin. Symptoms may take up to five hours to appear.
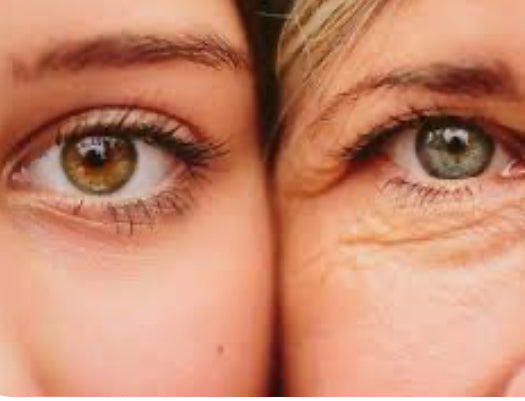
The negative effects of sunlight on skin: premature ageing
The sun is responsible for up to 90% of premature skin ageing
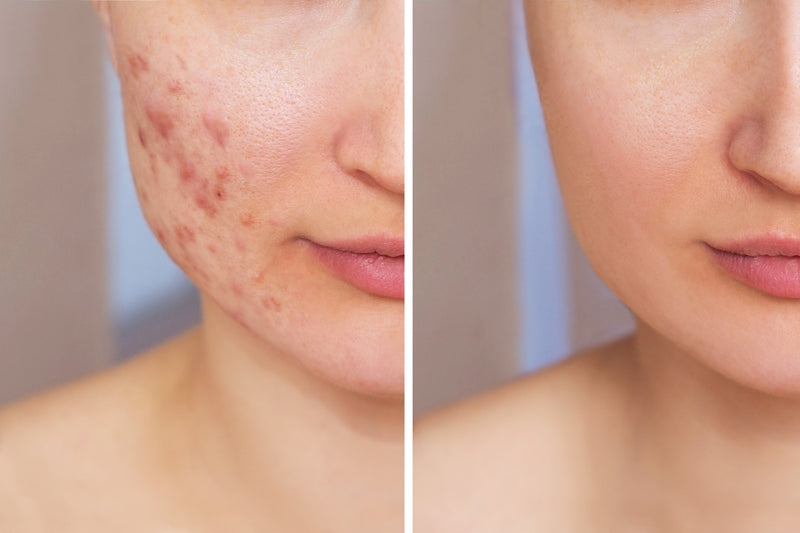
Skin ageing is, of course, an entirely natural process, but when skin ages prematurely it may start to sag and develop wrinkles before its time. Up to 90% of premature skin aging is thought to be caused by the sun1 and is known as photoaging. The direct DNA damage caused by UVB rays plays a role in photo ageing, but the main cause is the oxidative stress triggered by UVA rays and HEVIS light. The free radicals induced not only stress skin cells they also break down collagen and elastin which are important for smooth, plumped skin: wrinkles form, skin loses volume and hyperpigmentation issues such as sun spots (also known as age spots) appear prematurely. You can read more on this - Photoageing: what causes it and how can I prevent it > https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24160281/
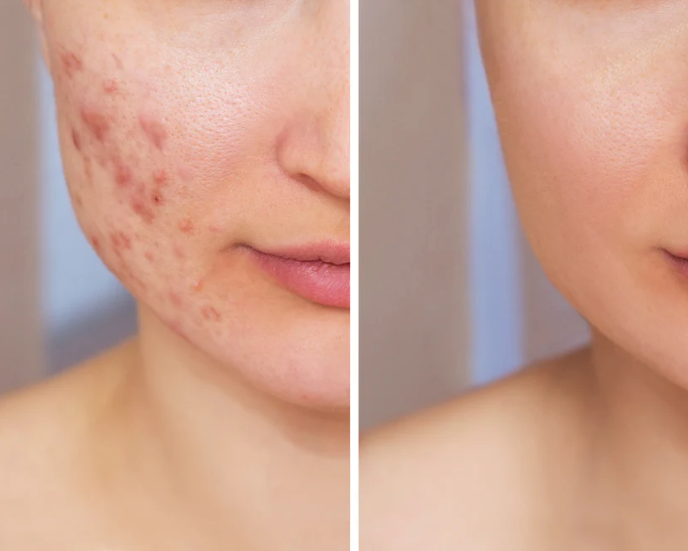
The negative effects of sunlight on skin: hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigmentation issues are triggered by overexposure to the sun
Hyperpigmentation is caused by an overproduction of melanin – the natural pigment that gives skin its colour. This overproduction can be triggered by a variety of factors but the most common is overexposure to the sun. UVA, UVB and HEVIS light rays are all connected with pigmentation issues and may contribute to conditions such as age spots (also known as sunspots) and melasma.
The negative effects of sunlight on skin: sun allergies. Symptoms of PLE appear one or two days after exposure to UV rays
Research suggests that a propensity to sun allergies is genetic, but that 80% of cases are triggered by UVA rays. When people have the underlying condition, their immune system identifies and reacts against areas of skin altered by the sun producing a rash.
What is Polymorphous Light Eruption?
- PLE causes a rash and skin redness
- PLE mostly effects young women and people with fair skin
The symptoms of Polymorphous Light Eruption (commonly abbreviated to PLE) range from a mild, bumpy rash through to skin redness, pustules, and blisters. Whatever the visual symptoms, skin is nearly always itchy. Symptoms tend to develop a day or two after being in the sun and are normally on the underside of the arms and the chest – facial skin can be affected, but this is less common.
PLE is most likely to effect young women and people with fair skin. It usually comes back each year when skin is first exposed to strong sunshine, but the causes are not limited to direct exposure: light passing through windows can also trigger the condition. The rash normally clears within a week if you stay out of the sun but, if exposure continues, symptoms may worsen.
The causes of PLE are not fully known but research suggests that it may be inherited. When people have the underlying condition, their immune identifies and reacts against areas of skin altered by the sun producing a rash: I see this condition as an allergy to UVA – so it’s important to use a high medical grade UVA protection.
UVA rays trigger 80% of cases of PLE
UV rays – especially long wavelength UVA rays (which trigger PLE in 80% of people affected) – penetrate deeply into the skin where they can damage cells.
UV-induced free radicals form highly reactive chemical compounds which cause oxidative stress, resulting in cell damage.
People with PLE have an impaired cellular defence which reduces their skin’s ability to handle these free radicals.
On exposure to the sun their skin responds by over activating its immune function, resulting in red and inflamed skin.
How can I prevent PLE?
Sun allergies can be prevented, or symptoms reduced, by careful sun protection: limit your exposure to the sun, avoid the peak hours when sun is at its most intense, wear protective clothing and use a sun protection product that offers high or medium protection and that has been specially formulated for your skin type and condition.
The negative effects of sunlight on skin: skin diseases
The UVB rays that lead to sunburn and damage the cellular DNA directly can, in the worst cases, cause skin diseases such as actinic keratosis (dry, red, or brown scaly patches of skin that can be painful but are harmless if treated) and skin cancer.
Physicians and dermatologists warn increasingly about the strong correlation between the sun and skin cancer. There are three main types of skin cancer:
Over exposure to UV rays is the primary source of skin cancer
Skin changes should be checked by a doctor or dermatologist.
Basal cell skin cancers appear as small, slow growing and shiny pink or red lumps. They are most frequently found on the face, scalp, ears, hands, shoulders and back.
Squamous cell carcinoma are usually pink lumps. They may have hard or scaly skin on the surface and are most often found on the face, neck, lips, ears, hands, shoulders, arms, and legs.
Melanoma is the most serious type of cancer. The first sign is often the appearance of a new mole or the change in appearance of an existing mole. Melanomas are more likely to have an irregular shape, be more than one colour and be larger than 6mm. They can be found anywhere on the body, but the back, legs, arms, and face are the most common locations.
If you are in any way concerned about moles or lumps on your skin consult your doctor.
Very important – you will never do microneedling or radiofrequency, on skin with visible skin changes – solar keratosis etc as there is a risk that there may be skin mutations going on in the skin - https://genomemedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13073-019-0648-4
What are the signs of skin ageing?
There are three main signs of skin aging and each one effects facial skin in a different way:
- Fine lines and wrinkles are usually the first visible sign of skin ageing.
- Sagging skin is a sign of loss of volume.
- As our skin loses elasticity it becomes less firm and deeper wrinkles form.
Wrinkles
The first noticeable signs of skin ageing are fine lines and wrinkles. Small, shallow wrinkles known as laughter lines or crow´s feet tend to become noticeable at the outer corners of the eyes. These may appear around the age of 30, but we all age differently and how we age depends on our genetics and lifestyle. These fine lines are followed by wrinkles on the forehead. At first these are only visible when our skin moves as we change our facial expressions, and they are known as dynamic wrinkles. As we age further, they become more prominent and evolve into permanent wrinkles that are visible even when our face is static. Frowning can cause vertical lines between the brows.
Loss of volume
It can be difficult to identify a loss of volume and facial contours. The first signs of a loss of volume in the lips tends to be when lipstick starts to bleed. A loss of facial volume tends to result in sagging skin, a flattening of the cheeks and the appearance of a “turkey neck”. It changes the overall appearance of the face which can look negative, sad, or tired. The fold that develops between the nose and the mouth, known as the nasolabial fold, is also linked to sagging skin and a loss of volume.
Loss of elasticity and deep wrinkles
As our skin matures its structure weakens and it loses elasticity and firmness. Skin also becomes drier, appears more `crepey` and loses the radiance we associate with youthful skin. Again, because our skin is as individual as we are, these changes become visible at different ages but are most experienced by those who are 50+
Finding it difficult to get an appointment with a skin doctor – this doctor is recognised as very good on skin and skin cancer. https://www.skincheck.ie/