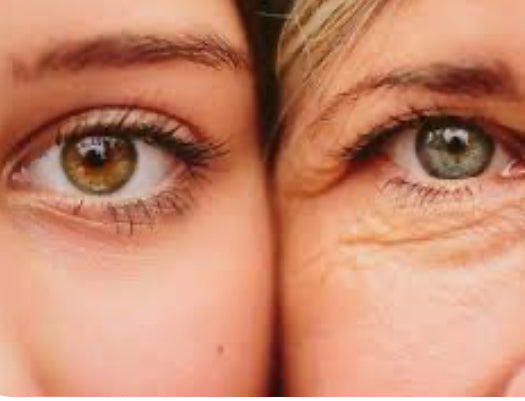
We are used to hearing about sun exposure and the damage that it can do to your skin. From skin cancer to sun related ageing , it can take its toll on the body. However, it is important to keep in mind that not all sun exposure is bad and, if done in moderation, can be good for you and your body.
However, before we get into the benefits, we should note that moderation is key here. Everyone should still take the proper precautions to protect themselves from Ultraviolet radiation, UV whenever they go outside and are at risk of being exposed to higher-than-safe radiation levels from the sun.
Benefits of moderate sun exposure
Sunlight can provide your body with a much needed serotonin boost
Serotonin is a type of hormone your body produces that is vital to good mental health. Sunlight and nighttime both trigger different hormones in your body. Sunlight triggers the production of serotonin, which helps you feel awake and produces feelings of positivity and relaxation. Darkness produces melatonin which is important for having a good sleep. Exposing yourself to the sun during the day, particularly in the morning, can help trigger the production of serotonin in your body and start your day off positively.
Sunlight can help you get a better night’s sleep
Exposure to moderate amounts of sunlight in the morning can also help you get a better night’s sleep. Sunlight in the morning resets your circadian rhythm. Studies have shown that exposure to sunlight in the morning can make it easier to fall asleep and wake up when needed. So getting out early in the morning or going for a nice walk can really help you sleep better at night.
Sunlight can help bolster your body’s natural immune system
Sunlight is one of the primary ways your body produces Vitamin D. Vitamin D is a key ingredient to a healthy body and is important in signalling the immune system, which helps your body monitor your cells. It has been linked with reduced infection rates and mortality rates.
Exposure to sunlight helps your body produce Vitamin D for other health benefits too
Aside from providing some foundations for a healthy immune system Vitamin D also has some other surprising and powerful effects on the body. Research has shown positive impacts on things like reduction of inflammation, healthy maintenance of muscles, stronger bones, improved brain function and lower levels of certain diseases like heart disease, prostate cancer and even dementia.
Sunlight can help lower blood pressure
High blood pressure can be dangerous and is linked to several health conditions like heart disease, kidney failure, and diabetes. The good news is that sunlight can help lower it by reacting with the nitrite oxide in the top layer of the skin, causing the blood vessel to widen and reducing the blood pressure in the rest of your body.
Vascular effects of dietary nitrate (as found in green leafy vegetables and beetroot) via the nitrate‐nitrite‐nitric oxide pathway
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3575935/
WHAT IS ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION?
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a type of light that is able to penetrate the earth’s atmosphere. Infrared and visible light are also part of this electromagnetic spectrum. Unlike visible light, however, UV radiation is invisible to the human eye because its wavelengths are too short. Further, it is broken down into three different categories, each based on unique wavelengths. These are:
- UVA, which have the longest wavelengths
- UVB, which have shorter wavelengths than UVA, but longer than UVC
- UVC, which have wavelengths that are so short, they cannot pass through earth’s atmosphere.
So when we talk about exposure to UV radiation, we’re really referring to UVA and UVB rays, as these are the two types that can penetrate the ozone layer and our skin.
Melanin absorbs the dangerous UV rays that can do serious skin damage.
This is the process that gives you a tan. A tan is a sign that your skin is trying to keep UV rays from damaging your skin. But melanin can't absorb all the UV rays.
Once melanin is produced by the melanocytes, it is then transported to cells called keratinocytes in the outermost layer of the epidermis by organelles called melanosomes. This is how your skin gets it colour, as well as how certain pigmentation issues such as sun spots, freckles and melasma appear.
Located in the undermost layer of the epidermis, melanocytes are the cells that produce melanin. Melanocytes are triggered to produce more melanin due to environmental factors such as exposure to UV light.
Melanocytes are also responsible for producing the melanin that gives your hair its colour , but these cells are more sensitive to the ageing process than those in your skin. This is why hair begins to grey with age, whereas the skin typically maintains its colour.
In the skin, there are two types of melanin:
- Eumelanin is black or brown pigment.
- Pheomelanin is a reddish-yellow pigment.
These different pigments, which occur in various concentrations, determine your skin and hair colour.
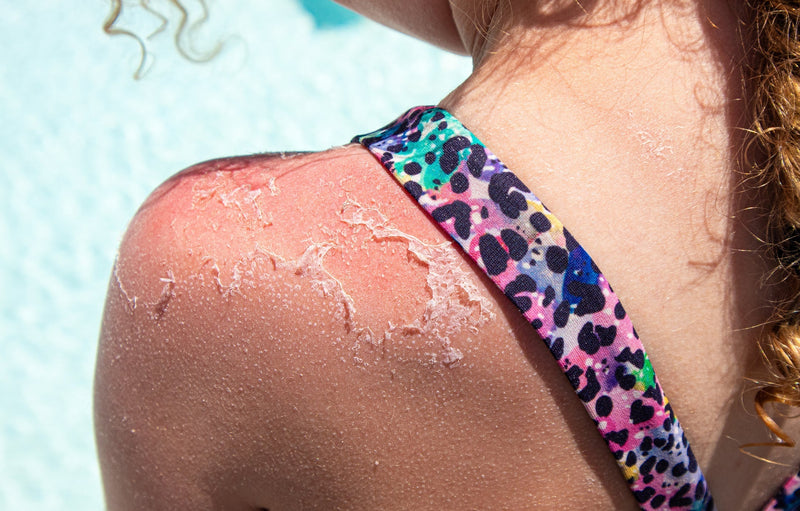
It is important to note that while the sun is not all bad for you - a tan is one of the worst things you can do for your skin, and it ramps up your chances of getting melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and other skin cancers.
We need to stress that everyone, no matter their skin colour or history, is vulnerable to UV rays and can develop skin cancer. However, certain demographics are statistically at higher risk of developing melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, or squamous cell carcinoma. These include:
- People with fair skin, pale eyes and hair.
- Anyone who spends a long time in the sun (for example, people who work in construction or outdoors .
- People with a family history of skin cancer.
- Those with immune system deficiencies.
- Anyone who had skin cancer before.
The Protective Role of Melanin Against UV Damage in Human Skin - PMC
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2671032/
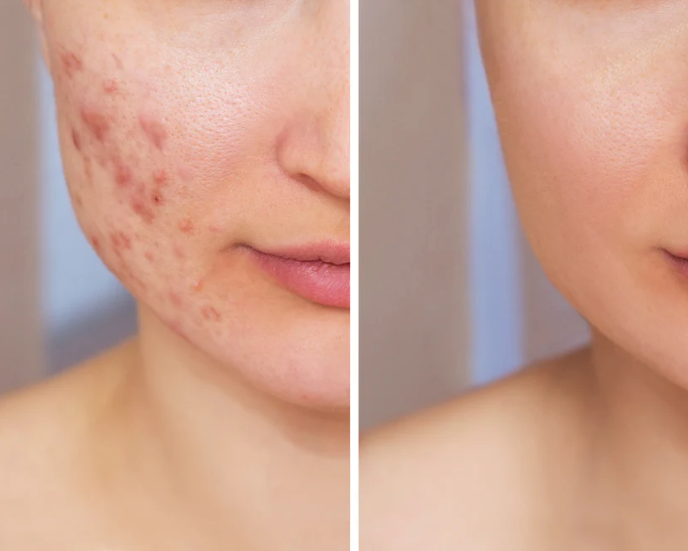
It is important to notice and changes in your skin , and have them seen to before they become too problematic to treat . Be aware of red spots that do not heal etc .
Ingredients that help to protect your skin.
L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
This is the only form of vitamin C you should look for in your skin care products. This is a science backed ingredient which helps to protect against environmental damage- apply under a quality broad spectrum SPF every day . it helps brighten skin and stimulates collagen.
There are many skin care products on the market today that boast vitamin C derivatives like magnesium ascorbyl phosphate or ascorbyl palmitate as an ingredient. But L-ascorbic acid is the only useful form of vitamin C in skin care products.
With age and sun exposure, collagen synthesis in your skin decreases, leading to wrinkles. Vitamin C is the only antioxidant proven to stimulate the synthesis of collagen, minimising fine lines, scars and wrinkles. It may also improve the appearance of sun-damaged skin. Initial use of vitamin C-containing creams can cause stinging or redness, but these side effects generally go away with continued use.
Retinol has the ability to repair damaged messages sent to your cell DNA .
Look to retinol to improve acne and acne scars, mottled pigmentation, fine lines and wrinkles, skin texture, skin tone and colour, and your skin’s hydration levels.
Retinol is considered the gold standard in anti-ageing and is the most researched skincare ingredient. Retinol is derived from vitamin A and is found in many over-the-counter anti-ageing products. Tretinoin, which is the active ingredient in prescription Retin-A and, is a stronger version of retinol. If your skin is too sensitive to use Retin-A, over-the-counter retinol is a better alternative.
Vitamin A has a molecular structure that’s tiny enough to get into the lower layers of your skin, where it finds and boosts collagen and elastin, which is a protein that strengthens your skin’s flexibility.